What Is Extended Detection and Response (XDR)? Definition, Components, Advantages, and Best Practices
Extended detection and response (XDR) enables a multi-layered approach to respond to cybersecurity issues by providing unified visibility across all security points. This article explains the fundamentals of XDR, its key components, and the top 10 best practices for deploying and managing an XDR system.
What Is Extended Detection and Response (XDR)?
Extended detection and response (XDR) is a security technology that safeguards IT infrastructure. It uses advanced analytics and machine learning techniques that combine data from endpoints, networks, cloud resources, email systems, and other relevant sources. It then builds a unique attack story based on that data. This simplifies the work of security analysts by offering enhanced visibility, quick threat analysis, and faster response.
In this article
XDR integrates several security products into a unified platform and a single interface. All of the data related to an attack can be easily viewed and provides a comprehensive view of multiple attack vectors. By providing a comprehensive view of your entire threat landscape, XDR strengthens your ability to detect and manage security incidents.
In addition, XDR eliminates redundant tasks required in a manual investigation of security incidents, irrespective of the targeted IT system. It helps your team uncover previously difficult-to-discover threats by eliminating siloed security solutions and products.
Today, several security companies adopt a layered security practice known as Defense-in-Depth (DiD), to secure different parts of their IT environment. This approach uses multiple security solutions such as endpoint detection and response, network traffic analysis, and security information and event management (SIEM) to safeguard endpoints, networks, and cloud systems.
Although DiD is an effective practice, it has certain drawbacks. Security systems operate in silos in an organization. For example, a typical security analyst handles only specific silos such as an endpoint or network. When attacks transition or move across silos or impact several IT systems concurrently, the layered approach fails to detect and respond to such attacks simply because it lacks the ability to do so. XDR tackles this problem effectively by offering a unified security platform that operates across security silos.
The operation of XDR can be summarized in three steps: data analysis, threat detection, and attack response.
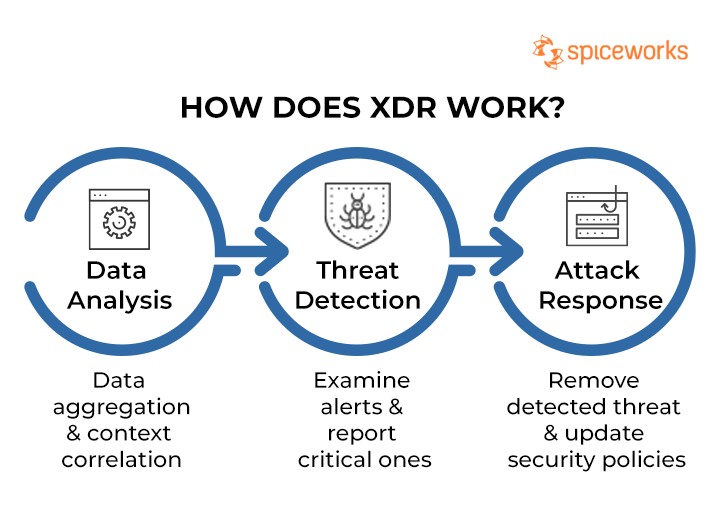
Three Steps of XDR
Step I: Data Analysis
XDR collects data from several security points, including endpoints, networks, servers, and the cloud. Upon data aggregation, it performs data analysis to correlate context from various alerts that are generated. This saves security teams from dealing with large volumes of security alerts and lets them zero in on high-priority signals or alerts.
Step II: Threat Detection
XDR offers excellent visibility into an organization’s IT infrastructure. This allows the system to examine signs of any detected threat and report the critical ones requiring a response. The visibility factor also enables companies to deep dive into the abnormal behavior of threats and investigate their origins before affecting other parts of the system.
Step III: Attack Response
In the last step, XDR primarily contains and removes any detected threats. Subsequently, it updates security policies to ensure that a similar incident does not reoccur in the near future.
Key Components of XDR
XDR is an evolved security system that extends the functionalities of traditional security tools such as EDR or NTA. These tools focus on security event correlation rather than event response. However, XDR is primed for instant incident response. An effective XDR system has six critical components that are considered a must by most organizations, which have been listed below.
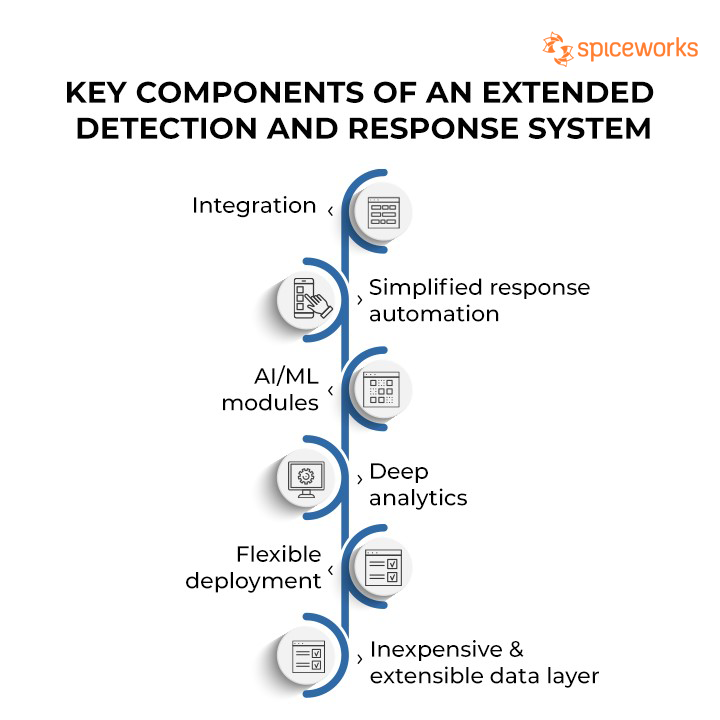
XDR Components
1. Integration with everything
The primary objective of XDR is to consolidate an organization’s security armory into a single, integrated solution. This implies that XDR solutions possess strong API-centric integration capabilities. XDR also needs to query any tool in the security stack for additional data and context and subsequently receive the data feed. Additionally, XDR also initiates immediate responses upon threat detection without requiring analysts to log in to another tool.
Integration serves as a key factor for any XDR solution because it adapts to the organization’s requirements instead of being limited to a vendor’s portfolio. Therefore, organizations must ensure they integrate new features into the XDR as they become available. They can quickly implement these developments themselves or rely on vendors for assistance.
2. Simplified response automation
Automation in XDR allows better threat detection and speeds up response outcomes. Security incidents such as malware or phishing attacks tend to repeat themselves. Response automation standardizes incident response based on the predefined playbook logic and delivers effective resolutions for known offenses. The automation intelligence in XDR thus adapts to the unique variables to a specific threat and automatically responds to them based on the associated risks.
3. AI/ML modules
AI in an IT environment drives XDR’s usability and adoption. With AI techniques, mathematical calculations are made on the fly to assess the threat and risk probability. Additionally, the XDR system learns about a specific environment, determines what modules to configure, and how to do it effectively. A potent XDR system with embedded AI/ML modules therefore learns, adapts, and also possesses the ability to deliver unique configuration guidance depending on what it learns from the business needs.
4. Deep analytics
A successful XDR deployment can distinguish between actual threats and false positives without letting the real attacks escape. A potentially good XDR ties threat data together and dynamically applies various analytical methodologies to detect, investigate, and verify the threat’s validity before initiating a response.
Good XDR systems, therefore, have the ability to assess the different tactics that an attacker may use to infiltrate an organization just by observing the pattern of every potential threat vector at one place or edge. This can enable the XDR to deliver deep threat detection and consequently generate an appropriate threat response.
5. Inexpensive & extensible data layer
Traditional SIEM storages are expensive as they are primarily built on outdated architectures. This is because the system finds it difficult to segregate near-term data necessary for threat detection and older historical data that aids in standardizing past threat trends. This implies that the data that needs no immediate analysis is still stored, making the overall storage system expensive as the volume of data grows with time.
On the other hand, an effective XDR can differentiate between the two data sources and, at the same time, employ low-cost methods to retain historical data records. Such XDR methods give access to older data without having to face any financial burden.
6. Flexible deployment
Each organization has its own XDR deployment requirements and preferences. Keeping this in mind, an XDR solution supports flexible deployments. It may be an on-premise and cloud-based implementation or managed deployments where organizations lack the requisite resources to manage them independently.
Typically, cloud-based and managed deployments support multi-tenancy features and stay compliant with certifications such as Service Organization Control 2 (SOC 2) to ensure that the platform operates in a secure environment. That being said, the requirements and preferences are subject to change over time. Hence, XDR needs to adapt and quickly migrate between two different deployment options.
Advantages of an Extended Detection and Response System
XDR offers a viable alternative to point security as it provides consolidated tooling to security teams, which allows them to watch over the organizational cybersecurity infrastructure more effectively. Its additional functionalities go beyond traditional EDRs, thereby giving it an upper hand in offering a holistic security solution to an organization’s IT environment.
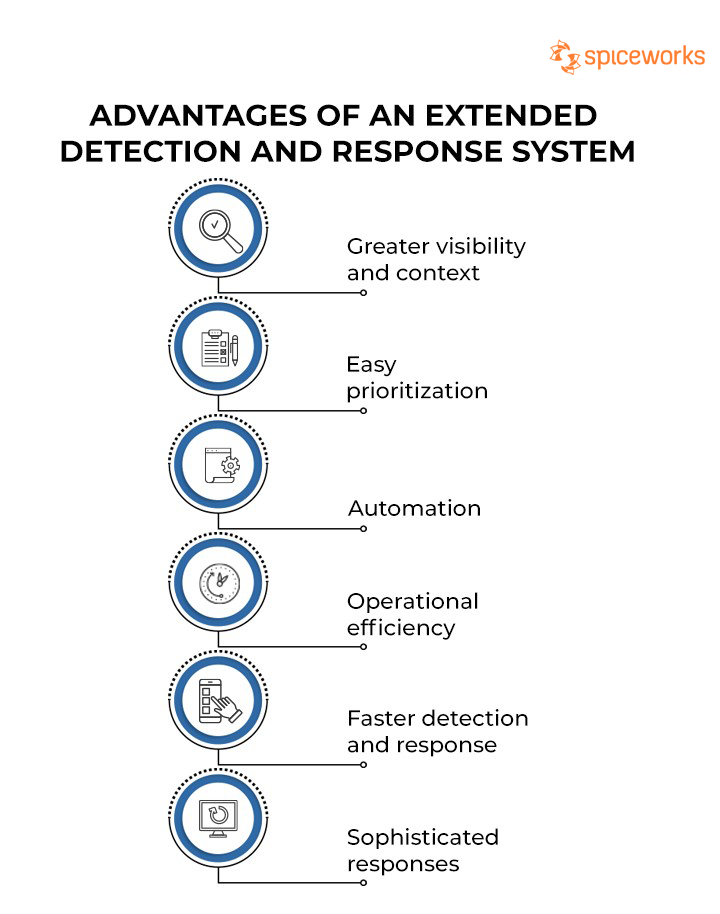
XDR Advantages
Benefits of XDR
1. Greater visibility and context
Compared to EDR and third-party security services limited to endpoints or workloads, an XDR system provides a 360-degree view of the organization’s security environment. It allows security analysts to view even those threats that utilize legitimate software to enter the organization’s boundary.
Security teams can use XDR to track threats at each security layer and subsequently note various parameters on how a particular attack happened, what the entry point of the attack was, who was affected by it, what the origin of the threat was, and how it spread.
2. Easy prioritization
IT and security teams are continually bombarded with thousands of alerts from different security services. As such, it becomes difficult to manage and optimize threat resolution. However, XDR’s data analysis and correlation capabilities allow security analysts to group alerts that relate to each other and prioritize them accordingly. Security teams can thereby focus on addressing the most critical threats by delaying the resolution of not-so-severe threats.
3. Automation
XDR’s automation support speeds up overall threat detection and response procedures. It eliminates the manual tasks involved in security processes. Thus, an XDR system allows IT teams to handle large volumes of security data at a particular time with enough room to perform complex processes redundantly.
4. Operational efficiency
Organizations employ a fragmented set of security tools to safeguard their infrastructure from attacks. On the other hand, XDR merges all these tools to give a holistic view of the threats across the environment. Moreover, it provides centralized data collection and threat response features coupled with the XDR environment, thereby offering a wider security cover to the entire IT ecosystem.
5. Faster detection and response
With all these advantages and the added operational efficiency of XDR, an organization enjoys an effective security posture. Deep contextual analysis allows the XDR system to identify the root cause of the threats and resolve them accurately at a faster pace. Today, quick threat detection and faster response are essential in a security landscape.
6. Sophisticated responses
Traditionally, EDR systems have responded to threats by isolating the target endpoint. The mechanism works fine when the endpoint is a standalone user device. However, if the endpoint is a server, it could pose a serious problem. XDR tailors sophisticated responses to specific systems with greater visibility and advanced capabilities. This leverages additional control points in an IT environment and minimizes the overall impact of the threats on it.
Companies such as Microsoft, Palo Alto, and Crowdstrike lead the pack when it comes to delivering XDR services, as the Forrester Wave for Extended Detection and Response (XDR), Q2 2024 names them as leaders from amongst 11 significant XDR providers.
Best Practices for Deploying and Managing XDR
An appropriately configured XDR system helps protect, detect, and respond to cyberattacks. To make the most of the deployed XDR system, organizations need to roll out the DiD strategy by setting XDR policies in line with the continually evolving security threat landscape.
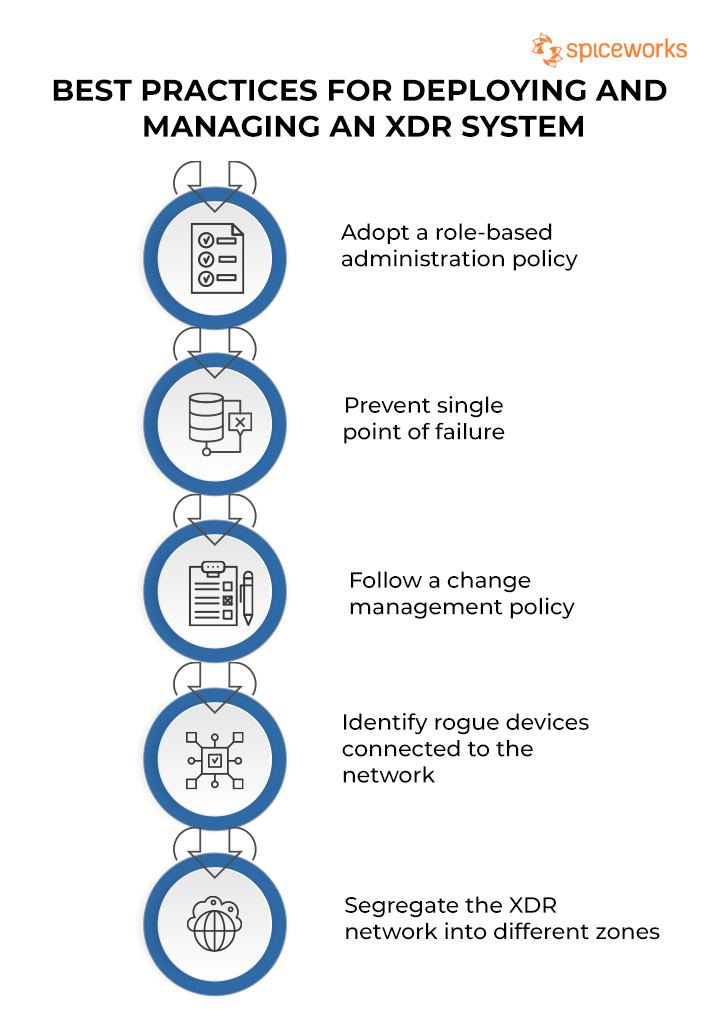
XDR Best Practices
1. Practice effective XDR management
XDR is an integral part of network and endpoint security, and it is important to have a good understanding of its commissioning process. Management of XDR involves general tasks such as upgrading, ongoing monitoring, and incident management. This requires considerable human resources, and organizations need to pay attention to it.
A not-so-well-managed XDR can easily misconfigure the whole XDR system, thereby affecting the network and associated devices adversely. Following are some of the management tasks to consider after deploying XDR:
- Document the XDR access control list and formulate the advanced firewall rules
- Adhere to the change management policy while changing XDR configurations
- Monitor firewall logs and intrusion detection & prevention system (IDPS) events
- Perform regular software updates and upgrades installed on appliances
- Set up a robust incident response plan depending on business use cases
2. Perform configuration backup
You should back up your current XDR configuration before making major changes. This will help you avoid potential misconfigurations, and give you something to roll back to should you discover an issue. Most systems include a configuration backup and restore application that is a companion to the bare-metal backup application. Additionally, you should consider encrypted backups of your XDR configurations to add an extra layer of security.
3. Adopt a role-based administration policy for XDR
An administrator application enables the creation of a robust, role-based XDR administration policy. These policies can restrict access to certain areas of the XDR while granting specific users read/write access rights based on their designated roles. Additionally, enforcing a least privilege policy ensures that users receive access rights tailored to their core functions.
4. Prevent single point of failure on the XDR network
XDR must actively use the ‘high availability’ feature to ensure continuity of services, irrespective of the possible node failures in the network. You can prevent a single point of failure on the network by placing two firewalls where the configuration of primary XDR is in sync with secondary XDR, .
Moreover, enterprises should focus on improving the overall quality of the service by ensuring that the resources at hand are available 24/7.
5. Follow a change management policy
Change management policy here refers to a formal process followed and implemented to make changes to the XDR configurations. Even so, XDR administrators should know the latest software versions available for upgrades.
Also, if you enable the automatic update feature, the XDR appliance will proactively look for new releases. This ensures your system is always using the latest information, which will improve the overall security.
6. Identify unknown or rogue devices connected to the network
Your organization should follow a standard process to identify and revoke unknown or rogue devices connected to the network. One way to achieve this is to scan the XDR network regularly and map all the devices by assigning them nicknames through the network map application. This allows the administrator to easily identify a new device as it would fall under the unmapped device category of the network map application.
7. Formulate a robust internet gateway security policy
It is crucial to configure a comprehensive internet gateway security policy on the XDR network as it minimizes the ability of hackers to attack the network. Consequently, setting a security policy will reduce the possibility of a bad actor accessing your network. With a policy in place, you can track down the attacker effectively should a breach occur.
Therefore, you should implement the following best practices when configuring and implementing the internet gateway security policy:
- Identify & block malicious applications on the network: This can be achieved by using XDR features such as application whitelisting, which use application-based rules to block any malicious application and permit access to only whitelisted applications.
- Secure the email gateway: Users behind the XDR system can be protected from email-related attacks such as phishing by configuring the email scanning gateway application.
- Scan the XDR directories for malware: This can be accomplished by using a malware file scanner app that scans various directories of the XDR for malware.
- Anti-phishing application: This application protects users from sites known to steal credentials and spread malware.
8. Segregate the XDR network into different zones
Network segregation is essential to ensure that attackers do not view the entire network as vulnerable. In turn, it restricts access to confidential information, credentials, services, and hosts. Your organization should segregate the XDR network into various zones, where any internet-facing server lies in a separate zone than the LAN network. Moreover, further segmenting LAN zones into subnets can make the network even more secure.
9. Formulate a comprehensive internet usage policy
A comprehensive internet usage policy makes users in the XDR network aware of the appropriate use of company assets. In addition, the web and protocol filtering capabilities of XDR can help you enforce these policies without user interaction.
Consider implementing the following web and protocol filtering settings:
- Global exception IPs: This enables administrators to quickly permit certain IPs and exclude them from different block categories.
- Global banned IPs: The content filter will block the designated host IPs from accessing the internet.
- Blacklisting website categories: This allows you to blacklist websites associated with specific subjects.
- Blocking content consisting of specific phrases: Once enabled, you can filter content to ensure no one accesses content that is inappropriate for your work environment.
- Blocking specific file extensions: This content filtering feature reduces the chances of end users downloading unapproved software, malicious content, or viruses.
10. Implement advanced firewall rules
Organizations should set up advanced firewall rules under “deny all traffic” and “permit-by-exception'”categories. Above all, you should determine which of the following factors apply to your organization:
- Risk assessment of incoming & outgoing network traffic: Risk analysis should be practiced for each permitted incoming and outgoing data flow.
- Permit rules specific to IPs and ports: Permit rules specific to ports (TCP/UDP), and IP addresses should be formulated.
- Firewall audit: XDR administrators should audit advanced firewall rules at regular intervals. This can be useful to identify unused rules and subsequently erase them.
- Firewall rule logging: It is recommended to log all firewall rules as it aids in auditing and network activity monitoring.
- Group firewall rules: Firewall rules should be classified under groups from WAN to LAN and LAN to WAN. This prevents human error and simplifies the administration of these firewalls.
Takeaway
The future of XDR looks bright. Markets And Markets predicts that the global XDR market will reach $8.8 billion by 2028, a growth rate of 38% over the 2023 market size. This prediction reflects how XDR benefits organizations and their ongoing security efforts.
XDR offers greater visibility in the organizational network and helps in breaking down security silos. It allows organizations to visualize the entire attack chain and quickly respond to them. Companies can readily use this knowledge to build playbooks that can help automate key processes designed to combat complex threats.






