What Is a Chatbot? Meaning, Working, Types, and Examples
A chatbot uses AI and automation to replace or augment human agents in customer service and engagement.
A chatbot is a conversational application that aids in customer service, engagement, and support by replacing or augmenting human support agents with artificial intelligence (AI) and other automation technologies that can communicate with end-users via chat. This article explains the meaning of chatbots in detail, their functionality, and types, with examples.
Table of Contents
What Is a Chatbot?
A chatbot is defined as a conversational application that aids in customer service, engagement, and support by replacing or augmenting human support agents with artificial intelligence (AI) and other automation technologies that can communicate with end-users via chat.
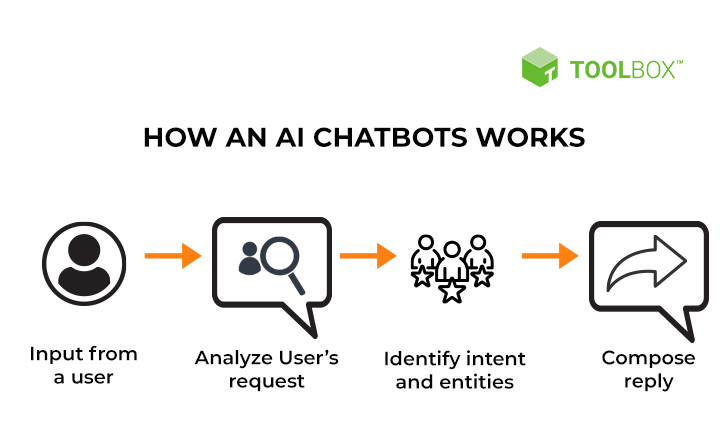
A Sophisticated Chatbot’s Inner Workings
Many businesses now use chatbots to automate user experience and transactional features. Organizations are experiencing considerable cost savings and have become more efficient as they reduce their reliance on support personnel and live operators.
Chatbots are computer programs that replicate and analyze human dialogue (spoken or written), enabling humans to communicate with electronic devices as if they were conversing with a live agent. Chatbots can range from simple programs that respond to a single instance to advanced virtual assistants that can learn and improve as they collect and process data to provide superior levels of personalization.
Chatbots are seamlessly integrated into several of our daily workflows. For instance, you could be browsing an e-commerce platform to purchase an item on your computer when a window appears on your monitor asking whether you require assistance. Alternatively, a person may use voice input to order a beverage from a nearby retail outlet and receive an alert indicating when the order would be ready and how much it would cost. These are some of the customer experience scenarios where one may encounter a chatbot.
The rise of chatbots in recent years is rooted in the accelerating pace of digital transformation. Businesses are increasingly migrating from traditional modes of communication to digital channels to interact and transact with their customers. Businesses use artificial intelligence (AI) to unlock new efficiencies in various customer-facing functions, and chatbots are among the top applications of AI in an enterprise.
As per Gartner’s 2022 predictions, 70% of white-collar employees will interact with chatbots and conversational platforms daily by the end of this year. This ranges from robotic advisors for personal use (like Google Assistant and Alexa from Amazon) and chatbots integrated into messaging applications like Facebook Messenger and WeChat.
Businesses can benefit from chatbots because they increase performance and save costs while enabling customer convenience and offering additional services to internal staff, clients, and partners. They allow businesses to quickly answer various issues across stakeholders while decreasing the need for human involvement.
Companies can scale, personalize experiences, and be proactively available using a chatbot, a key differentiator in the digital era. When a business relies exclusively on human effort, for instance, it can only service a certain number of people at a time – which limits capacity and puts a ceiling on growth. Companies with manual-effort-intensive processes are compelled to rely on highly rigid models to be cost-effective, which means that their proactive and customized outreach possibilities are limited.
On the other hand, chatbots enable companies to interact with a virtually endless number of clients in a personalized way, to be scaled up or down based on current requirements. One can provide an almost “humanlike” service tailored to each individual, even as the chatbot is deployed to millions of customers at the same time.
How Does a Chatbot Work?
To understand how a chatbot works, we must first consider the three core mechanisms driving the technology. The three mechanisms that require your attention are rules-based processes, AI-driven decision-making, and live agent intervention. Depending on a chatbot’s mechanism, its functionality will be slightly different.
How do chatbots using rules-based processes work?
Rules-based chatbot software performs pre-programmed behaviors based on “playbooks” you create on the user interface’s backend module. Like a digital assistant, rules-based chatbot technology can behave in a certain way based on click activities and simple event triggers like a “yes” or a “no” input. It may also detect a specific keyword or combination of phrases (but only when there is an exact match).
For instance, you could program a rules-based chatbot to answer not only if someone chooses “black” or “white,” but also if they say “I want a black item” – the chatbot’s backend module will match the term black with a preconfigured rule.
How do chatbots using AI-driven decision-making work?
Artificial intelligence chatbots employ AI and natural language processing (NLP) technology to recognize sentence structure, interpret the knowledge, and improve their ability to answer questions.
Instead of relying on a pre-programmed response, AI chatbots first determine what the customer or user is saying. Then, once they have figured out what the user is looking for, the chatbot provides an answer that it believes is correct based on the available data. The machine learns the “right” response over time by analyzing correct and erroneous responses.
With AI-driven decision-making mechanisms, a chatbot can be extremely effective, provided they have a thorough understanding of your organization, its customers, and its context. This functionality is primarily used by large enterprises like e-commerce as well as other high-volume businesses that demand scale.
How do chatbots using live agent interaction work?
Live chat is a type of chat system that sits on the webpage or in your mobile application and works as a consumer’s window to your support team and contact center. Using this mechanism, chatbots incorporate routing capabilities to assign discussions in real-time.
When a customer needs to communicate with a representative from your team, the chatbot scans agent availability and routes the discussion request accordingly. It will connect the customer with someone who can help them with their problem – i.e., an agent with the right skills and knowledge. The chatbot also alerts the agent when there is a customer query and informs the customer about agent details like their name, waiting time, etc.
As you can see, these processes are relatively understandable, given that advancements in chatbot technology today are endless and readily accessible to users and developers alike.
See More: Top 10 Speech Recognition Software and Platforms in 2022
Types of Chatbots
Hundreds of thousands of businesses worldwide are developing diverse forms of chatbots intending to enhance customer service. This section explains the various types of chatbots, what they are used for, and which chatbot software could be the most beneficial to your company.
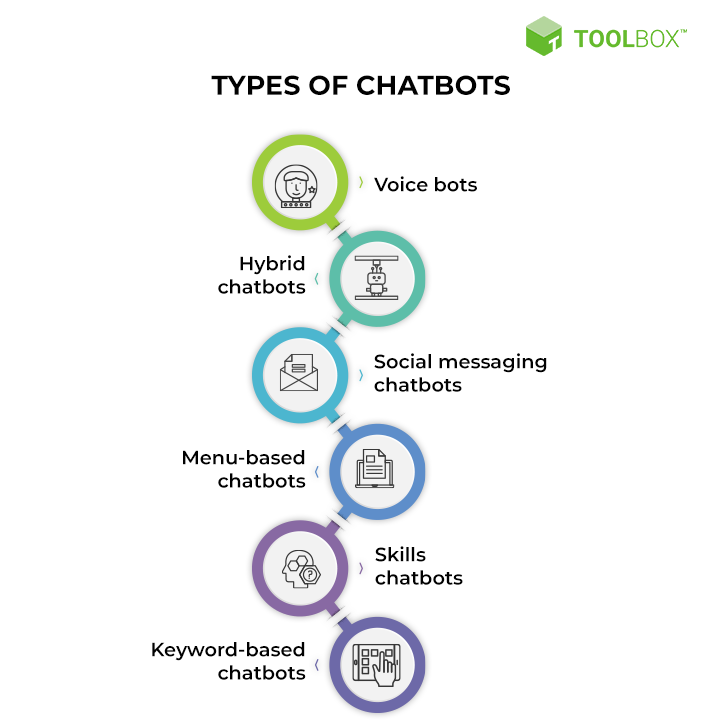
Types of Chatbot
1. Voice bots
A voice bot is a voice-to-text and text-to-speech communication channel powered by AI and natural language understanding (NLU). AI technology aids in identifying key speech signals and determining the optimal conversational response. The text-to-speech (TTS) engine subsequently completes the interaction by converting the message into audio or voice.
These bots are programmed to complete the entire speech comprehension and response process in a human-like manner. Voice assistants or voice chatbots provide a sophisticated model of communication that one may quickly implement into various customer service tools, including interactive voice response (IVR), self-service, and online knowledge bases.
2. Hybrid chatbots
A hybrid chatbot is a harmonious blend of chatbot and live chat that combines the best of both worlds. A customer service representative will be available in live chat to answer any customer’s questions, which may be too complex or nuanced for automation alone.
An AI component in a chatbot replicates conversations based on how it is programmed and the needs of the conversation. On the other hand, a hybrid chatbot will initiate an automated chat conversation and attempt to resolve the user’s query as quickly and simply as possible. If it does not function as expected, a customer service representative can intervene at any moment or in the subject matter area where the chatbot cannot complete the task.
3. Social messaging chatbots
With the rise of new social media interfaces, organizations can now deploy an AI algorithm across all of their customer’s preferred messaging platforms. This includes Facebook Messenger, Twitter, Instagram, as well as messaging apps like WhatsApp and WeChat. It enables a more pleasant online experience for customers and increased engagement for the company – all without adding to a contact center’s workload.
4. Menu-based chatbots
The most rudimentary type of chatbot in use is one that is based on menu-driven navigation. Most of the time, these chatbots follow a fixed decision tree that is displayed to the consumer in the form of clickable buttons. These chatbots (like the automated dial pad menus on telephones that we use regularly) ask the user to make several choices and click on suitable options to get to the final solution.
Although these chatbots are adequate for addressing frequently asked questions, which account for most support requests, they may fall short in more complicated scenarios. If there are too many elements or too much expertise at play, the menu-based chatbot may not be able to help users arrive at the correct response. It is also important to note that menu-based chatbots are the slowest to deliver genuine value to the consumer, but they are simple and affordable to get started.
5. Skills chatbots
A skills chatbot is another kind of bot that can perform a specific set of tasks, once you have extended its capabilities using pre-defined skills software. For example, the chatbot may be able to provide weather information, turn off your room lights when connected to a smart home appliance, order groceries online, etc. With access to the skill’s source code, developers can construct their own skills chatbots and integrate them with other platforms.
6. Keyword-based chatbots
Keyword-based chatbots can listen to what visitors enter and answer correctly, unlike menu-based chatbots. These chatbots use customizable keywords and NLP to detect action triggers in the conversation to understand how to respond appropriately to the consumer. However, when faced with many similar inquiries, these chatbots may fall short. The chatbots could begin to falter if there are keyword repetitions across numerous associated inquiries.
That is why chatbots that combine keyword identification and menu or button-based navigation are becoming increasingly popular. If the keyword detection functionality fails or the user needs additional help finding an answer, such chatbots give users the option of directly entering commands via clickable navigation buttons. This is an effective workaround when the bot cannot detect keywords in the typed input.
7. Rules-based chatbots
A rule-based chatbot is ideal for companies that already know the types of inquiries their customers will ask. Chat flows are created by using if/then logic, and you must first establish the chatbot’s language requirements. Conditions for evaluating words, word structure, synonyms, and more are the essential tenets of its functionality. Customers will receive prompt assistance if an inbound inquiry falls within these parameters.
It is important to note that it is the developer’s responsibility to cover every permutation and combination of a query as much as possible – or else, the chatbot will not be able to understand the consumer or respond to them.
8. AI-powered contextual chatbots
Contextual chatbots can grasp the context of a chat and determine the correct meaning of the user inquiry. It can also recall prior interactions and use that information to maintain relevance while interacting with repeat customers. Contextual bots can guarantee that repeat users have a consistent experience. Furthermore, it may retain information on user intent gathered across numerous platforms and channels, ensuring that the conversation’s context matches the needs of the consumer at every touchpoint.
Contextual chatbots are connected to the centralized database of a site or app, typically a customer relationship management (CRM) system or a customer data platform (CDP). This enables them to retrieve critical information about an individual with whom they are chatting, such as the individual’s name, location, or purchase history.
9. Support chatbots
Support chatbots are conversational systems designed solely to provide customer support and post-purchase services. Unlike bots on social media or websites, they do not share offers, promos, or other customer engagement materials. This type of chatbot is typically found on self-service portals and online documentation, where users might come to receive support and help. Support chatbots are widely used for internal purposes, including answering HR queries, raising IT tickets, submitting employee documents, etc.
10. Transactional bots
Transactional chatbots can help organizations strengthen their sales and marketing efforts, whether for appointment scheduling, lead generation, or payment collection. Users can conduct transactions directly while conversing with the chatbot without human intervention.
Its biggest benefit is the ability to enable transactions and drive business 24/7/365. As a result, a transactional chatbot differs from other types of bots, like informational or support bots. Its focus is to complete a transaction and streamline the user experience by offering a quick and easy channel for a single purpose. It is designed to handle a small number of specialized tasks.
11. No code or low code chatbots
Chatbots have traditionally been designed and developed using code to create decision trees and AI and machine learning (ML) algorithms powering the technology. Each programming language has a web API that one can use to build chatbots. In addition to PHP and Node.js, many other libraries that enable Python or Java are used in most typical deployments.
However, recent advancements allow organizations to use chatbots that require little or no coding. This allows for speedier application delivery and faster value generation since a graphical user interface (GUI) is available to build and configure the bot. No-code deployments are suitable for information-collecting chatbots and those that encourage human interaction. In contrast, low-code chatbots are ideal for organizations that need to add unique features while reducing development efforts.
See More: Data Science vs. Machine Learning: Top 10 Differences
Top 5 Examples of Chatbots in 2022
One can find examples of chatbot implementations in nearly every major company with a digital presence. Here are five examples of the top ways you may use chatbot technology in discrete industries and use cases.
1. Lead generation chatbots on websites
These chatbots utilize a conversational technique to acquire information on website visitors, help customers through the purchase process, or qualify prospects. They help users navigate through multiple options and allow companies to engage with prospects proactively, ensuring they do not abandon your website. Lead-generating chatbots are effective for building relationships with website visitors and engaging with them 24 hours a day, seven days a week.
2. Information and application submission chatbots in the insurance sector
Insurance providers can employ chatbots to connect with consumers, provide policy quotations, gather insurance premium contributions, upsell and cross-sell products and services, and more. This can either be rule-based or use artificial intelligence and natural language processing. Additionally, insurance – and the financial services sector – have relied heavily on human agents. Chatbots allow insurance providers to reach a much wider audience and make it easier for customers to process their claims.
3. Virtual assistants for information search on smartphones
A large number of smartphone users employ voice assistants like Google Now, Cortana, Siri, and Alexa to look up information regularly. The virtual assistant will listen to you, respond, and perform tasks such as sending a mail, conducting searches, opening apps, providing weather information, and so on. An important benefit is that you can use voice to control virtually anything through voice-to-text and text-to-speech options.
4. Customer support chatbots on e-commerce applications
Chatbots are transforming the e-commerce industry and enabling merchants to provide better purchasing experiences. They simplify a broad matrix of complex relationships and move business forward as part of a more extensive transformation to automate operations and adopt technologies that support customer care. E-commerce apps use chatbots to keep customer experiences entirely online and reduce the need for one-on-one interactions.
5. Bill payment bots by utility companies
Chatbots also allow utility companies to deliver on-demand customer support without relying solely on actual teams of customer service agents, which became critical, especially during the covid pandemic. Chatbots significantly impact bill payments – the customer can enter their service ID, and the bit will automatically fetch their most recent invoice. Using transactional systems, customers can pay their dues directly on the app without visiting the utility company’s office. This ensures uninterrupted service and timely payments.
See More: Is Intelligent Automation an Alternative to RPA? Experts Weigh In
Takeaways
Chatbots are now an essential part of business operations, streamlining both internal and customer-facing interactions. Basic chatbots use a simple rules-based navigation system to solve customer queries. More complex systems rely on AI, Ml, and NLP to understand a customer’s unique context to provide an effective resolution. Organizations can integrate chatbots with their existing digital platforms and contact center solutions to provide high-quality support to a large number of customers.
Did this article help you understand a chatbot’s functionalities? Tell us on LinkedIn, Twitter, or Facebook. We’d love to hear from you!
MORE ON AI
- How Does Artificial Intelligence Learn Through Machine Learning Algorithms?
- Top 10 AI Companies in 2022
- How Is AI Changing the Finance, Healthcare, HR, and Marketing Industries
- What Is Narrow Artificial Intelligence (AI)? Definition, Challenges, and Best Practices for 2022
- Top 10 Machine Learning Algorithms






